The Physical Education Program in the Extracurricular Hour to Improve Physical Fitness for Boys 14-15 Years Old
2 Deparment of Physical Education, An Giang University, Vietnam
3 Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Received: 06-Sep-2021 Accepted Date: Sep 13, 2021 ; Published: 31-Dec-2021
This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits reuse, distribution and reproduction of the article, provided that the original work is properly cited and the reuse is restricted to noncommercial purposes. For commercial reuse, contact reprints@pulsus.com
Abstract
Aim: This study aims to find and evaluate an experimental approach to developing the strength of 14–15-year-olds in extracurricular fitness and health classes at the gym. Materials & Methods: Classes are based on a circle training form, they are held three times a week, taking into account the students' age-specific strength development and performing complex strength exercises using How to use equipment to simulate and exercise with local and regional exercise exercises. The randomized method is used to select a group of students aged 14-15 years (60 people) to participate in experimental classes in the school's physical education system (supplemental). Research Results: The positive influence of the experimental program on the training and development of strength competencies (dynamic, static) of students (male) aged 14-15 in the context of supplementary physical education at school has been being established. By the end of the trial period, the number of students with "average" and "above average" physical health increased and the number of young men with "low" strength development levels decreased. The proposed test method increases the student's fitness level, as evidenced by the increase in the motor test score values. The value of the elastic index of young men increases by 20%, the speed is 12.48%, the endurance is 10.26%, and the speed-strength increases by 7.75%. The number of young men with "average" and "high" levels of the value of the motor test indicators increases. Conclusion: Proposing experimental methods to develop the physical capabilities of 14-15-year-old students in school gymnastics is highly effective and can be encouraged to improve the fitness and physical capacity of the student.
Keywords
Strength capacity; Strength training; Gymnastics; Physical fitness
Introduction
In recent years, an increasing number of students in Vietnam, and some other countries are interested in forms of extracurricular physical activity. [1,2] This indicates a decrease in motivation for traditional forms of classroom organization and the need to modernize physical education in educational institutions. [3,4] One of the forms of organizing advocacy activities according to the student’s choice is supplementary physical education. [5] In this regard, in our opinion, the mission is to develop methods and technologies to develop the strong competencies of high school students in physical education, sports in sports, and sports groups. Physical enhancement is essential. This issue has not been fully addressed in the scientific literature, which reduces the effectiveness of 12th-grade capacity development training sessions.
A certain level of strength development is required in all major sports. In young men, a high degree of strength development is a prerequisite for successful service in the military. [1,5] Meanwhile, according to various studies, about 80% of young men and women, after graduating from high school, have low physical characteristics. Improving health and developing healthy lifestyle habits are priorities in the physical education of young people in many different countries. [6] Reduction Youth advocacy activities in recent decades in several countries [7] and physical educational performance. [8] Therefore, the issue of youth actively participating in physical training and sports is one of the State’s policy priorities in many countries. Research on physical culture shows that physical development, one of the main motor qualities of a child’s body, has a significant impact on overall physical development.
This fact shows the need to improve the effective educational and referral process technology and curriculum for regular and extracurricular activities that develop the strong competencies of high school students. Scientific literature analysis has shown that a lot of material has been accumulated on the choice of media and methods to develop the strengths of high school students. Physical training of students is done in many forms of physical education (regular, extracurricular).
The research purpose of the topic is to find and evaluate an experimental method to develop physically effective 14-15-yearold students during class time in the practice room.
Methodology
A randomized method was used to form a 14-15-year-old group of 60 people to practice in the school gym using an experimental approach to improving strength. Before and after the pedagogical experiment, the male students’ endurance abilities were assessed by dynamic endurance tests: Pull-up on a high crossbar, (times); pull-over, (times); dig-up on the bars, (times); lifting the torso from the supine position, (times/min); standing long jump, (cm); throwing a 3 kg stuffed ball with two hands sitting from behind the head, (cm). Static strength tests were performed: Exercises needle, (s); bun (Ball), (s); half-squat, (s); plank, (s); handgrip and deadlift dynamometry tests (kg). Motor tests were used to assess speed, endurance, speed and strength abilities, and flexibility: Running 100 m, (s); running 1500 m; jumping rope 30 sec, (times); leaning forward from a standing position with straight legs on a gymnastic bench, (cm).
The training sessions are held in 4 phases, three times a week, for 90 minutes, from August 2019 to March 2020. Fitness is selected to suit individual teenagers’ possibilities. Classes follow the circular method of training.
In the main part of the unit, students are asked to do groups of local and regional empirical exercises with recommendations 99 [Table 1].
| Basic exercises | Sets per exercise | Amount of repetition | Loading (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st day (Monday; from 15-00 till 16-30.) | Alternate standing dumbells curl with hand supination |
2 | 20 | 8 |
| Standing row | 3 | 10-12 | 35 | |
| Alternate standing dumbells curl with the neutral position of hand hammer |
2 | 20 | 8 | |
| Abdominal raise from the support position on elbows on bars |
3 | 10 | Sole weight | |
| Walk (6 min.) on a treadmill 1 | 1 | - | Sole weight | |
| Latpulldown | 4 | 8 | 50 | |
| 2nd day (Wednesday; from 15-00 till 16-30) | Dig-up on the bars | 3-4 | 4-5 | Sole weight |
| Lying tricep extension on a horizontal bench | 4 | 12 | 25 | |
| Lifting the torso from the supine position | 3 | 15-20 | Sole weight | |
| Pec deck in «Butterfly» training simulator | 2-3 | 12-15 | 30 | |
| Standing lateral raise with dumbells | 4 | 10-12 | 8 | |
| Walk (6 min) on a treadmill | 1 | - | Sole weight | |
| 3rd day (Friday; from 15-00 till 16-30) | Push-ups | 3 | 20 | Sole weight |
| Leg extension in a training device | 3 | 10-12 | 50 | |
| Superextention (hyperextention) | 3 | 12-15 | Sole weight | |
| Walk on a treadmill | 1 | - | Sole weight | |
| Squats (front squat, overhead squat, back squat) |
4 | 10-12 | 20 | |
| Leg curl in a training device | 3 | 12-15 | 30 |
Table 1: Contents of the program to develop male strength abilities with the use of exercise equipment.
In the early stage (first 2 months), circular exercise is used to strengthen the musculoskeletal system and increase the functioning of the male body, as well as to provide a basis for increased load. The impact intensity is 40%-45% of the maximum, the number of repetitions in the approach-15-25 for the basic development of endurance, number of stations-6-12, number of rounds-1-3. The work phases are arranged as follows: 15 seconds-work, 45 seconds- rested; 15 seconds-work, 30 seconds-rested; 30 seconds-work, 30 seconds-rested.
For the next 2 months (phase II), we used intensive alternate training methods to develop strength with local exercises. At this stage, the load intensity is 50%-65% is the maximum, the working time in each exercise is 15-30 seconds, the number of repetitions in the approach is 8-12 reps. The interval between approaches is 50-90 seconds, the station number is 4-10, and the lap number is 1-2.
In the third stage, to increase the load intensity and the differential effect on the lagging muscle groups, the successive series method is used. When doing exercises with local weights, we use weights 50%-70% maximum, increasing the number of approaches and repeating with a 40-60 second resting interval. When doing area exercises, you should do 2-4 repetitions 12-15 repetitions with a pause between sets of 60-120 seconds.
In the final stage IV, a combination of circular and repetitive exercise methods was used to produce distinct effects on muscle groups. The young men perform 2-3 series of exercises at stations 4-6. [9] Consent from the boy’s parents to conduct the survey.
To statistically analyze the obtained results, the application software Microsoft Excel and SPSS 20.0.
Results
After the experiment, the boys showed statistically significant increases in all indicators of dynamic and static strength, handgrip, and dead lift dynamometry [Table 2].
| Tests | Indicators | t | P | (W%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before the experiment (M±SD) | After the experiment (M±SD) | |||||||
| Dynamic strength | Lifting the torso from the supine Position (times/min) | 42.2 | 4.96 | 49.5 | 5.21 | 2.28 | <0.05 | 15.92 |
| Pull-up on a high crossbar ( times) | 8.2 | 3.52 | 11.43 | 4.22 | 2.49 | <0.05 | 32.91 | |
| Standing long jump (cm) | 184.5 | 7.22 | 217.4 | 6.52 | 3.06 | <0.05 | 16.37 | |
| Pull-over (times) | 1.6 | 1.39 | 2.82 | 1.73 | 2.26 | <0.05 | 55.20 | |
| Dig-up on the bars (times) | 7.94 | 3.42 | 10.9 | 4.25 | 2.31 | <0.05 | 31.42 | |
| Throwing a 3 kg stuffed ball with two hands sitting from behind the head (cm) | 258.2 | 3.75 | 286.9 | 4.45 | 2.82 | <0.05 | 10.53 | |
| Static strength | Half-squat, (s) | 52.3 | 4.12 | 73.5 | 4.38 | 2.45 | <0.05 | 33.70 |
| Plank (s) | 29.78 | 2.46 | 45.7 | 2.98 | 2.31 | <0.05 | 42.18 | |
| Bun (Ball) (s) | 38.6 | 2.87 | 55.4 | 2.95 | 2.01 | <0.05 | 35.74 | |
| Needle (s) | 40.4 | 3.56 | 59.06 | 4.23 | 2.45 | <0.05 | 37.52 | |
| Dynamometry | Right hand (kg) | 38.89 | 2.86 | 41.93 | 3.59 | 2.44 | <0.05 | 7.52 |
| Left hand (kg) | 34.38 | 4.68 | 38.69 | 4.97 | 2.28 | <0.05 | 11.80 | |
| Deadlift (kg) | 156.45 | 4.31 | 172.28 | 4.98 | 2.56 | <0.05 | 9.63 | |
Table 2: Young men's strength indicators values before and after the experiment (M ± SD).
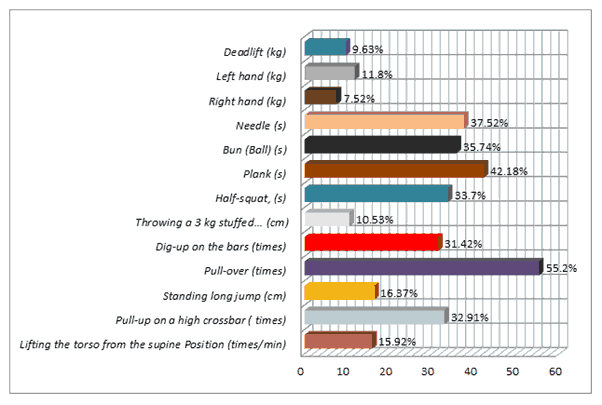
The highest value (55.20%) of the increase in the young men’s dynamic strength was set in the test pull-over (time). The lowest value (10.53%) of the increase was in the test throwing a 3 kg stuffed ball with two hands sitting from behind the head (cm). The values of the static force indicators increase exceeded 35% of the initial level. The values of the increase in handgrip and deadlift dynamometry indicators were about 9%.
At the end of the trial, the number of young adults with a growth rate is shown in [Figure 1].
Discussion
The search for new and improved traditional approaches to increase the efficiency of fitness classes for students continues to be relevant. [10,11] It confirms the importance of research. choose ours. Since students’ motivation for generally accepted methods of physical activity is still low, [12] some researchers propose organizational methods. is different from the student’s physical education. Researchers propose to use time-based intensive training and fitness technology [13] more widely in school physical education. Increasing physical activity, in addition to regular fitness classes, has a positive impact on students’ physical health, [14] according to data from our study. The results of using the proposed program to develop strength for boys aged 14-15, using exercise equipment show that by the end of the trial, the number of students with average physical health up and down. among young people, there is a ‘low’ level of power development. Using the circle exercise method in the proposed program to enhance male strength increases the motor and emotional density of the classes, making the classes varied and enjoyable. taste more. Use the student’s physical education approach to supplemental physical education. Holding significantly increases youth stamina and overall fitness performance.
We believe that one of the reasons that increase the mobility, static, and strength of the arms and body is the value of the indices in the motor tests at the end of using our test method. The proposed increase is an increase in young men’s physical motivation associated with an additional form of extracurricular physical education. This is consistent with survey results of Hispanic students, studying 1-2 years in secondary education institutions. They point out in their survey of important temporal activities outside of the classroom, regarding a growing interest in this form of a physical education organization. [15] Other researchers especially recommend spending significant time on extracurricular physical activity, [16] which increases not only the physical but also the mental as a result. Other authors observed, an increase in the indicators of students’ cognitive and physical functions. [17] This statement is consistent with data obtained by other researchers. [11] We believe that researching capacity development in the physically complementary learning environment of students is a promising direction of the program to enhance the fitness of modern students.
| Physical condition tests | Before the experiment (M ± SD) | After the experiment (M ± SD) | t | P | W% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Running 100 m (s) | 14.98 | 3.22 | 13.22 | 3.19 | 2.28 | <0.05 | -12.48 |
| Running 1500 m (min, s) | 7.58 | 4.36 | 6.84 | 3.89 | 2.39 | <0.05 | -10.26 |
| Jumping rope 30 sec.(times) | 62 | 3.75 | 67 | 3.65 | 3.15 | <0.05 | 7.75 |
| Leaning forward from a standing position with straight legs on a gymnastic bench (cm) | 9 | 6.23 | 11 | 7.09 | 3.26 | <0.05 | 20.00 |
Table 3: Students' physical condition tests indicators' values before and after the experiment (M ± SD).
Conclusion
The experimental method we developed and tested to develop the physical capacity of 14-15-year-old boys using exercise equipment in the supplementary physical education system at school has become a useful method. useful. Significant in enhancing students’ mobility and stillness of hand development and measuring dynamics. At the end of the test, an increase in the values of the indexes of the motor tests in terms of speed, general endurance, speed endurance, and active flexibility of the spine is found. The proposed program to develop the competencies and endurance of 14-15-year-old males expands theoretical knowledge in the field of physical and sports education and it can be introduced for use in institutions other education.
Conflict of Interest
The authors and planners have disclosed no potential conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge all volunteers who participated in the study and the volunteer who permitted us to use her photograph
REFERENCES
- Thuc DC. Building the model of recreational sports club for students of an Giang University, Vietnam. IJMHS. 2019;9(4):384-394
- Thuc DC. (2018). The effect of physical activities on biological age parameters of females from 17 to 18 years old. J Sports. 2018;5(1):7-11.
- Ferreres ZA, Alguacil MY, Pascual GF. Analysis of the opinion on physical education in high schools and the extracurricular sports practice of students and their personal environment. J Phys Educ Sport. 2018;18(3):646 –653
- Andrieieva O, Yarmak O, Palchuk M, Hauriak O, Dotsyuk L, Gorashchenco A, et al. Monitoring the morphological and functional state of students during the transition from middle to high school during the physical education process. J Phys Educ Sport. 2020;20(3):2110–2117.
- Dugnis PY, Milkhin VA, Romanova EV, Peregudova TM. High-speed power training of students in physical education and sport classes. Phys Cult Sport. 2020,2(18):149-158.
- Roman M. Effectiveness of the complex movement program of physical training for professional soldiers. J Phys Educ Sport. 2018;18(3);1773-1778.
- Görner K, Reineke A. The influence of endurance and strength training on body composition and physical fitness in female students. J Phys Educ Sport. 2020;20:2013–2020.
- Olafsdottir AS, Torfadottir JE, Arngrimsson SA. Health behavior and metabolic risk factors associated with normal weight obesity in adolescents. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(8):24-28.
- Hortigüela AD, Pérez-Pueyo Á, Moncada-Jiménez J. An analysis of the responsibility of physical education students depending on the teaching methodology received. J Phys Educ Sport. 2015;15(2):202-207.
- World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki-Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. 2013.
- Kolumbet AN, Dudorova LY. Correction of physical education program for technical higher educational establishment girl-students on the base of their health indicators. Phys Educ Stud. 2016;20(6):18-25.
- Natal'ya M, Kolokoltsev M, Romanova E, Alontsev V, Ustselemov S, Strashenko V, et al. Program for improving strength abilities of 16–17-year-old students in the additional physical education system. J Phys Educ Sport. 2020;20(5):2796 – 2802.
- Drachuk S, Bohuslavska V, Pityn M, Furman Y, Kostiukevych V, Gavrylova N, et al. (2018). Energy supply capacity when using different exercise modes for young 17–19- year-old men. J Phys Educ Sport. 2018;18(1):246-254.
- Valery Z, Olena S, Hanna T, Volodymyr S. (2020). Fitness technologies in the system of physical qualities development by young students. J Phys Educ Sport. 2020;20(1):142–149.
- Munir T, Ifet M, Eldin J, Denis S, Haris A, Rasim L, et al. Quantitative changes of specific motor abilities of students under the influence of regular and additional activities in sport and physical education. IJKSS. 2015;8 (2):34-37.
- Ferreres ZA, Alguacil MY, Pascual GF. Analysis of the opinion on physical education in high schools and the extracurricular sports practice of students and their personal environment. J Phys Educ Sport. 2018;18(3):1646 –1653.
- Codina N, Pestana JV, Castillo I, Balaguer I. Ellas a estudiar y bailar, ellos a hacerdeporte: Unestudio de las actividades extraescolares de los adolescent esmediante los presupuestos de tiempo. Cuadernos de Psicologíadel Deporte. 2016;16(1):233-242.



 The Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research is a monthly multidisciplinary medical journal.
The Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research is a monthly multidisciplinary medical journal.